GPT摘要
本文介绍了一个基于Java实现的支持事务的简易关系型数据库系统。该系统主要包含以下核心功能: 1. 数据库基本操作 : - 实现了包括遍历(Scan)、连接(Join)、聚合(Aggregation)和增删改查等基本数据库操作算子 - 使用直方图统计信息进行查询优化,估算查询成本并确定最优的连接顺序 2. 存储管理 : - 设计了三级存储结构:HeapPage(存储元组)、HeapFile(管理数据文件)和BufferPool(缓存管理) - 实现了基于LRU的页面淘汰机制 3. 事务与并发控制 : - 实现了页面级的共享锁、排他锁和锁升级 - 采用严格两阶段锁协议保证可串行化 - 实现了三种死锁检测算法:超时检测、等待图检测和全局优先级检测(wait-die) 4. 恢复机制 : - 基于UNDO日志实现STEAL/NO-FORCE缓冲区管理策略 - 实现预写日志(WAL)机制,支持事务回滚与恢复 - 通过日志记录数据修改的前后镜像,确保事务的原子性和持久性 系统采用模块化设计,包含完整的数据库组件:表结构管理(Catalog)、查询处理(Operator)、存储管理(HeapFile/Page)和事务管理(LockManager/LogFile),是一个教学性质但功能完备的数据库系统实现。
simple-db code:Goinggoinggoing/simple-db-hw-2021 (github.com)
基于java语言,实现一个简易事务支持的关系型数据库
难度:lab4 = lab5 > lab6 >>>>>> lab3 > lab2 > lab1
lab1 实现基本的数据结构
lab2 实现scan iterator
基于scan iterator 来实现各种聚合函数,比如avg,count,sum,join等
lab3 join 优化
建立一个优化模型, 按照主键,非主键,scan 表代价,直方图等进行成本估计,根据估计值来确定多表join的顺序
lab 4 事务以及锁
这一章相对较难,要自己实现一个简单的读写锁,但是6.830中简化了,实现了page-level的锁,粒度比较粗,还有多种死锁的情况,test很给力,建议在写的时候一定要看清楚是哪个transaction 拿到了哪些page的哪些lock,而且这里的代码会影响到后面的lab 5、6,这里主要是按照两阶段锁协议并且no steal / force 的策略
代码中实现基于Timeout 、Wait-for Graph 、 Global Orderings (wait-die)死锁检测算法
lab 5 B+ 树索引(TODO)
实现B+树索引,插入、删除、修改,难点在于要把B+树结构以及这三种操作逻辑要捋清楚,还有父节点,子节点;叶子兄弟节点,非叶子节点的指针问题,以及一些边界条件。
lab 6 实现基于 log的rollback 和 recover
lab中并没有真正存在undo log 和redo log,日志结构比较简单,只需要根据偏移处理即可,可以理解成是逻辑上的undo log 和 redo log。基于UNDO日志实现STEAL/NO FORCE 策略,提供更灵活的缓冲区管理;实现基本的WAL(Write-Ahead Logging)策略实现事务回滚与恢复
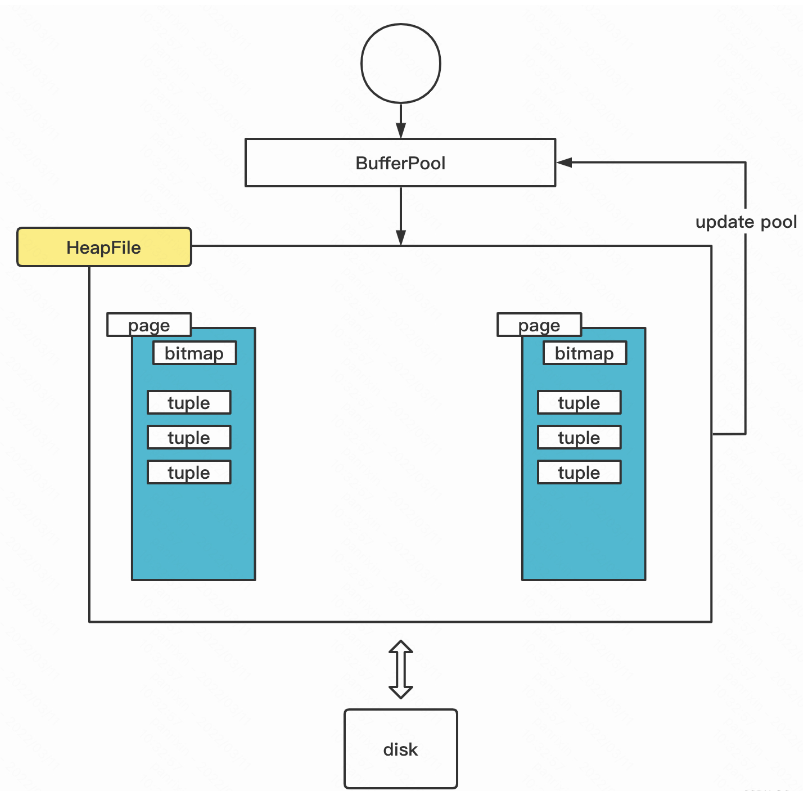
lab1 Database Catalog Table(DbFile,多个page) HeapPage( []Tuple ) Tuple( []Field) Field
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 Tuple:一行记录的内容private TupleDesc tupleDesc;private Field[] fields;private RecordId recordId; table-page-slotprivate List<TDItem> tdItems; TDItem(fieldType, fieldName)public HashMap<Integer, Table> tables; key是DbFile.getId() 也就是tableid,hash(path)private Map<PageId, Page> pageCache;8 ) / (_tuple size_ * 8 + 1 ))1.0 / 8 );HeapFile (File f, TupleDesc td) ;return new HeapPage ((HeapPageId) pid, buffer);implements OpIterator 对HeapFile包装, 为最基础的select * int tableid, String tableAlias; 包含别名,'chaining them together.' Special access method operators at the leaves of the plan are responsible for reading data from the disk (and hence do not have any operators below them) .this operator then calls getNext on its children, and so on, until these leaf operators are called. They fetch tuples from disk and pass them up the tree (as return arguments to getNext) ; tuples propagate up the plan in this way until they are output at the root or combined or rejected by another operator in the plan.this lab, you will only need to implement one SimpleDB operator.
HeapPage:
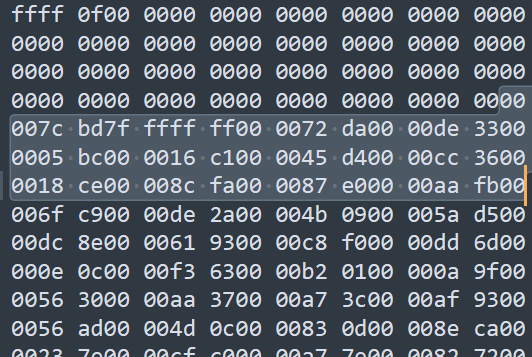
对于一个只有两个int的表,单个page中,共4096B的数据,Tuple行数为4096* 8 / 8*8+1 = 504行,headsize=504/8= 63B
也就是前63B都是head(484个空),数据为00007cbd、7fffffff。创建过程在HeapPageReadTest.java
总结 数据获取,txt转为HeapPage可读取的文件格式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 4066 *8/3*4*8+1 = 337 337 /8 = 43B 原始数据 java -jar dist/simpledb.jar convert some_data_file.txt 3 1 ,1,1 2 ,2,2 3 ,4,4 .bat 0000 0111 第一个byte低三位代表有三个tuple 0700 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 00 |00 0000 0100 0000 0100 0000 0100 0000 0200 0000 0200 0000 0200 0000 0300 0000 0400 0000 0400 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public static void main (String[] argv) {new Type []{ Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE };new String []{ "field0" , "field1" , "field2" };TupleDesc descriptor = new TupleDesc (types, names);HeapFile table1 = new HeapFile (new File ("some_data_file.dat" ), descriptor);"test" );TransactionId tid = new TransactionId ();SeqScan f = new SeqScan (tid, table1.getId());try {while (f.hasNext()) {Tuple tup = f.next();catch (Exception e) {"Exception : " + e);
lab2 基本操作,需要继承Operator,实现fetchNext, Operator implements OpIterator
基于装饰器模式,
Filter 和某个field比较,并过滤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Predicate(int field, Op op, Field operand)public boolean filter (Tuple t) 将传入的tuple和构造函数中的值比较true next () 方法获取下一个,依靠fetchNext,需要重写while (child.hasNext()){Tuple next = child.next();if (predicate.filter(next)){return next;return null ;@Test public void filterSomeLessThan () throws Exception {this .scan = new TestUtil .MockScan(-5 , 5 , testWidth); new Predicate (0 , Predicate.Op.LESS_THAN, TestUtil.getField(2 )); Filter op = new Filter (pred, scan);MockScan expectedOut = new TestUtil .MockScan(-5 , 2 , testWidth);
Join 根据JoinPredicate规定的列是否满足op
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 JoinPredicate(int field1, Predicate.Op op, int field2)for 遍历child1 child2,留下满足条件的。为了配合实现迭代器,需要额外记录下外层tuple1while (child1.hasNext() || tuple1 != null ){if (tuple1 == null ){while (child2.hasNext()){Tuple t2 = child2.next();if (joinPredicate.filter(tuple1, t2)){Tuple tuple = new Tuple (getTupleDesc());int i = 0 ;while (fields.hasNext()){while (fields.hasNext()){return tuple;null ;return null ;scancost (t2) ntups (t2)
Aggregate min max sum count avg
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 IntegerAggregator(int gbfield, Type gbfieldtype, int afield, Op what) 分组idx 分组类型 聚合idx'male' -> ('male' , 10 )'female' -> ('female' , 8 )IntegerAggregator agg = new IntegerAggregator (0 , Type.INT_TYPE, 1 , Aggregator.Op.SUM);
1 2 3 4 Aggregate(OpIterator child, int afield, int gfield, Aggregator.Op aop);Aggregate op = new Aggregate (scan1, afield=0 , gfield=0 ,
insert delete 共HeapPage HeapFile BufferPool三层
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 HeapPage: Tuplepage ,所以pid要改成当前HeapPage的,slot按插入的位置来Page > (注意操作的page 是从pool中拿,会修改pool 但不修改文件)page (需要修改file 文件的大小,也就是写入空数据,然后再从pool中拿) 实验中tuple2int,一个page504条,超出后自动增一page log ().getDatabaseFile(tableid); 需要把设置返回的为dirty 事务层面page 可以写504条数据
Page eviction 对于一个2个int的表,共1024*504条数据,也就是1024个page,没有eviction全部存入时63MB ,50pages 3MB
evictPage:扔掉前flush
随机 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private synchronized void evictPage () throws DbException {if (iterator.hasNext()){PageId pid = next.getKey();Page page = next.getValue();if (page.isDirty() != null ){
FIFO 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Override public void modifyData (PageId pageId) {if (set.contains(pageId)) return ;@Override public PageId getEvictPageId () {PageId peek = queue.poll();return peek;
LRU: 双向链表+Hash
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public class LRUEvict implements EvictStrategy {public void LRUEvict () {new HashMap <>();new Node (null );new Node (null );@Override public void modifyData (PageId pageId) {if (hashMap.containsKey(pageId)){Node node = hashMap.get(pageId);else {Node node = new Node (pageId);@Override public PageId getEvictPageId () {Node prev = tail.prev;return prev.pageId;public void addHead (Node node) {public void moveToHead (Node node) {private void removeNode (Node node) {class Node {public Node (PageId pageId) {this .pageId = pageId;
flushPage(pid): 如果pid脏的,就写回磁盘discardPage(pid):直接扔掉某一个page
总结 1 2 3 4 5 SELECT * FROM some_data_file1,WHERE some_data_file1.field1 = some_data_file2.field1AND some_data_file1.id > 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public static void main (String[] args) {new Type []{Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE};new String []{"field0" , "field1" , "field2" };TupleDesc td = new TupleDesc (types, names);HeapFile table1 = new HeapFile (new File ("lab2_file1.dat" ), td);"t1" );HeapFile table2 = new HeapFile (new File ("lab2_file2.dat" ), td);"t2" );TransactionId tid = new TransactionId ();SeqScan ss1 = new SeqScan (tid, table1.getId(), "t1" );SeqScan ss2 = new SeqScan (tid, table2.getId(), "t2" );Filter sf1 = new Filter (new Predicate (0 ,new IntField (1 )), ss1);JoinPredicate p = new JoinPredicate (1 , Predicate.Op.EQUALS, 1 );Join j = new Join (p, sf1, ss2);try {while (j.hasNext()) {Tuple tup = j.next();catch (Exception e) {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 int table1Id = Database.getCatalog().getTableId("t1" )SeqScan ss1 = new SeqScan (tid, table1Id, "t1" );Filter sf1 = new Filter (new Predicate (0 ,new IntField (1 )), ss1);Aggregate ag = new Aggregate (sf1, 1 , 2 , Aggregator.Op.SUM);JoinPredicate p = new JoinPredicate (1 , Predicate.Op.EQUALS, 1 );Join j = new Join (p, sf1, ss2);
Query Parser 读取表数据 并运行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 java -jar dist/simpledb.jar parser catalog.txt lab2_file1 (f1 int , f2 int , f3 int ) lab2_file2 (f1 int , f2 int , f3 int ) select d.f1, d.f2 from lab2_file1 dwhere 语句报错?
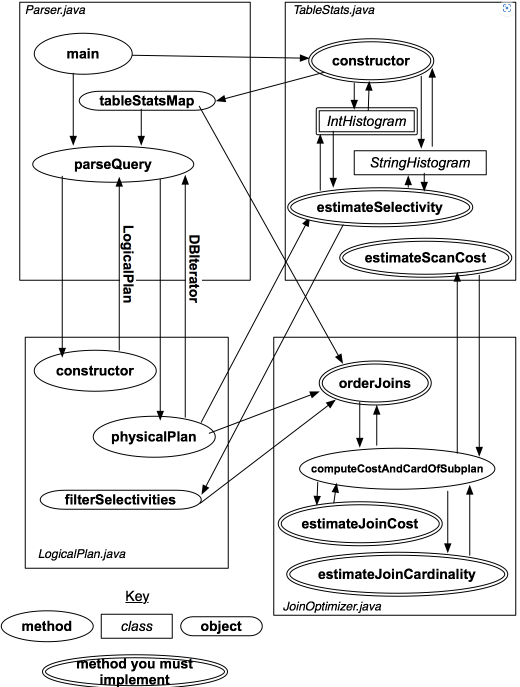
lab3
通过分析表的统计信息,可以估算不同查询计划的成本。计划的成本与中间连接和选择的元组数量、过滤器和连接谓词的选择性相关。
使用这些统计数据 order joins and selections to get an optimal way
selectivity: 筛选比例
在这个实验中,我们只关注连接和基本表访问序列的成本。我们不必担心访问方法的选择(因为我们只有一种访问方法,即表扫描),也不必考虑其他操作符(如聚合)的成本。
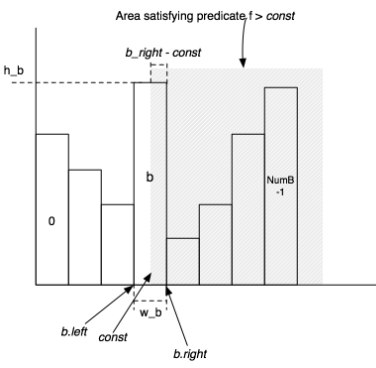
Filter Selectivity base on histogram,to get ntups with one or more predicates
f=const :h/w f>const :h_b x (b_right - const) / w_b + buckets( b+1…NumB-1)
1 2 3 4 private int [] buckets;public IntHistogram (int buckets, int min, int max) public void addValue (int v)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 private Map<Integer, IntHistogram> intHistogramMap;private Map<Integer, StringHistogram> stringHistogramMap;public TableStats (int tableid, int ioCostPerPage) public double estimateSelectivity (int field, Predicate.Op op, Field constant) public double estimateScanCost () {return numPage * ioCostPerPage;
1 2 private static final ConcurrentMap<String, TableStats> statsMap = new ConcurrentHashMap <>();
Join cardinality estimate the size (ntups) of t1 join t2
for equality joins, primary key > non-primary key
For range scans > non-primary key equality 估值product*0.3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public int estimateJoinCardinality (LogicalJoinNode j, int card1, int card2, boolean t1pkey, boolean t2pkey, Map<String, TableStats> stats) {switch (joinOp) {case EQUALS:if (t1pkey && !t2pkey) {else if (!t1pkey && t2pkey) {else if (t1pkey && t2pkey) {else {break ;case NOT_EQUALS:if (t1pkey && !t2pkey) {else if (!t1pkey && t2pkey) {else if (t1pkey && t2pkey) {else {break ;default :int ) (0.3 * card1 * card2);
Join cost p=t1 join t2 join ... tn
1 2 3 scancost(t1) + scancost(t2) + joincost(t1 join t2 ) +scancost(t3) + joincost((t1 join t2 ) join t3 ) +
scancost(t1) : the number of pages in t1 x SCALING_FACTOR
joincost(t1 join t2): = scancost(t1) + ntups(t1) x scancost(t2) //IO cost
+ ntups(t1) x ntups(t2) //CPU cost
1 2 3 public double estimateJoinCost (LogicalJoinNode j, int card1, int card2, double cost1, double cost2)
Join order 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class CostCard {public double cost;public int card;public List<LogicalJoinNode> plan;public List<LogicalJoinNode> orderJoins ( Map<String, TableStats> stats, Map<String, Double> filterSelectivities, boolean explain) throws ParsingException {PlanCache planCache = new PlanCache ();CostCard bestCostCard = new CostCard ();int size = joins.size();for (int i = 1 ; i <= size; i++) {for (Set<LogicalJoinNode> subset : subsets) {double bestCostSoFar = Double.MAX_VALUE;for (LogicalJoinNode joinNode : subset) {CostCard costCard = if (costCard == null ) {continue ;if (bestCostSoFar != Double.MAX_VALUE) {if (explain) {return bestCostCard.plan;
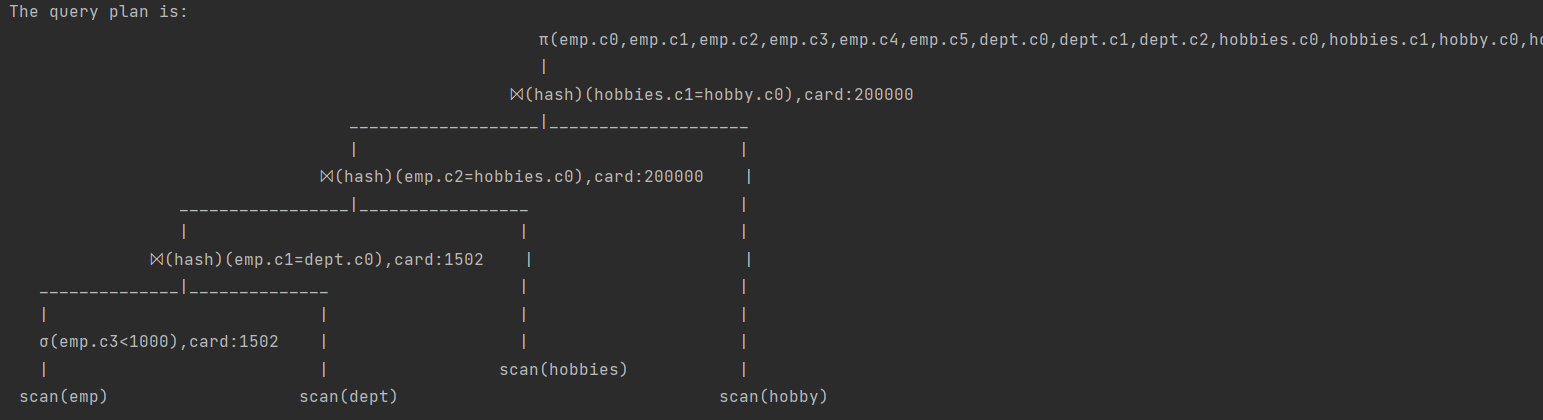
"SELECT * FROM emp,dept,hobbies,hobby WHERE emp.c1 = dept.c0 AND hobbies.c0 = emp.c2 AND hobbies.c1 = hobby.c0 AND emp.c3 < 1000;"
emp过滤后1500: 随机数最大值65530,1500≈(1000/65535*10w)
lab4 A transaction is a group of database actions (e.g., inserts, deletes, and reads) that are executed atomically ;
Atomicity : Strict two-phase locking and careful buffer management ensure atomicity.Consistency : The database is transaction consistent by virtue of atomicity. Other consistency issues (e.g., key constraints) are not addressed in SimpleDB.Isolation : Strict two-phase locking provides isolation.Durability : A FORCE buffer management policy ensures durability (see Section 2.3 below).
核心思想:NO STEAL/FORCE
To simplify your job, we recommend that you implement a NO STEAL/FORCE buffer management policy.
You shouldn’t evict dirty (updated) pages from the buffer pool if they are locked by an uncommitted transaction (this is NO STEAL).
由于只在最后刷盘,不需要undo了,失败只要重新从磁盘加载page即可
On transaction commit, you should force dirty pages to disk (e.g., write the pages out) (this is FORCE).
假设transactionComplete不会失败,这样就不需要redo log
lock acquire acquire and release locks in BufferPool
Modify getPage() to block and acquire the desired lock before returning a page. 核心方法,阻塞获取锁
Implement unsafeReleasePage(tid, pid). This method is primarily used for testing, and at the end of transactions. 释放tid在pid上的锁
Implement holdsLock(tid, pid) so that logic in Exercise 2 can determine whether a page is already locked by a transaction. tid是否锁住pid
create data structures that keep track of which locks each transaction holds and check to see if a lock should be granted to a transaction when it is requested:hashmap: pageid->locks
插入 删除 查找都是调用pool的getPage,需要传入正确的permission
被操作的页置为dirty
插入时创建了新的page,能否正常锁定
release strict two-phase locking:This means that transactions should acquire the appropriate type of lock on any object before accessing that object and shouldn’t release any locks until after the transaction commits.
release a shared lock on a page after scanning it to find empty slots
NO STEAL 只evict非脏页,都是脏页就抛出异常。AbortEvictionTest testAllDirtyFails()测试
transactionComplete commits or aborts
途中可能抛出TransactionAbortedException 请求超时,死锁 如readpage
commit:写回磁盘 释放锁
abort:重新从磁盘加载page 释放锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public void transactionComplete (TransactionId tid, boolean commit) { if (commit) {else {
AbortEvictionTest测试 :如果abort 插入的行是否还能找到
Deadlocks and Aborts detect deadlock and throw a TransactionAbortedException,被捕获后调用transactionComplete
a simple timeout policy(或者retry次数过多)
check for cycles in a dependency graph
全局排序:每个事务分配一个全局序号 WAIT-DIE (当前高就wait、否则rollback;保证环路中优先级最低的一定die) WOUND-WAIT
或者资源分配一个序号 哲学家,在这里代表着pageid 不好实现 因为pageid的读取顺序和业务相关
可能会中止本该成功的事务
DeadlockTest.java
t1读p1 t2读p2,然后t1写p2(等t2) t2写p1(等t1),就死锁了
TransactionTest.java
n个进程,首先都获取读锁,然后再进行一次删除和插入
锁升级时就会出现死锁等待
timeout 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();long timeout = new Random ().nextInt(2000 ) + 1000 ;while (true ) {if (lockManager.acquire(pid, tid, perm)) {break ;long now = System.currentTimeMillis();if (now - start > timeout) {throw new TransactionAbortedException ();100 );
cycle check 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 while (!lockManager.acquire(pid, tid, perm)){new Random ().nextInt(10 )); if (next.getValue().getLockType() == LockType.EXCLUSIVE || perm == Permissions.READ_WRITE){TidNode tidNow = tidMap.getOrDefault(tid, new TidNode (tid));new HashSet <TidNode>(), tidNow);return false ;private void checkCycle (HashSet<TidNode> visited, TidNode tidNode) throws TransactionAbortedException {if (visited.contains(tidNode)){throw new TransactionAbortedException ();if (tidNode.next != null ){
wait-die 可以保证环路中,优先级最低的一定die
需要遍历全部资源冲突的(否则会失效),如果存在优先级高的则die
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 boolean unlock = true ;while (iterator.hasNext()){if (next.getKey().equals(tid)){continue ;if (next.getValue().getLockType() == LockType.EXCLUSIVE || perm == Permissions.READ_WRITE){if (tid.getId() > next.getValue().getTid().getId()){throw new TransactionAbortedException ();false ;if (!unlock){return false ;
进阶:能否在获取失败后wait而不是自旋? wait的锁住的对象不好处理 用map<PageId, PageId>尝试失败
lab5 lab6
之前的pool中的脏页不能写回磁盘(NO STEAL),现在提供undo解决这一问题
commit后如果宕机怎么办?先写入日志,日志实现恢复
You will implement rollback and recovery using the contents of the log file.
undo:记录下修改 用于 abort
redo:恢复成功的事务
STEAL and NO-FORCE:提供更灵活的缓冲区管理,允许commit前写回磁盘
abort时,先根据日志把磁盘中的数据还原,再删除pool中的该页面,最后把pool中的脏页recover
基本配置 因为可能没有commit就写回了(缓存空间不足 ,测试中通过flushAllPages模拟),需要写回前记录下写回前后的内容信息。当commit后,需要更新旧的信息
Insert the following lines into BufferPool.flushPage() before your call to writePage(p), where p is a reference to the page being written: 在page写回磁盘前,先将log写回,包含最开始的内容(BeforeImage)以及当前内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 TransactionId dirtier = p.isDirty();if (dirtier != null ){if (page.isDirty() != null ){false , null );
在commit并刷盘后,更新BeforeImage,
1 2 3 4 5 flushPages(tid)
先debug,查看在什么情况下会写log
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 static final int ABORT_RECORD = 1 ;static final int COMMIT_RECORD = 2 ;static final int UPDATE_RECORD = 3 ;static final int BEGIN_RECORD = 4 ;static final int CHECKPOINT_RECORD = 5 ;static final long NO_CHECKPOINT_ID = -1 ; 日志文件开始logCommit (tid) 提交事务
log格式:type 和 tid, 内容 , 最后写offset
1 2 3 4 5 6 raf.writeInt(ABORT_RECORD);
RollBack logFile/rollback():事务回滚后,把改事务修改的page还原到之前的状态
修改了但已经写回磁盘:pool中存在但已经不是dirty(flushPage会写回磁盘并删除脏页标记)
根据log找到该事务修改的pageId,读出before-image, 并写回( tidToFirstLogRecord map到第一个log)
删除pool中的页面(这里丢弃了页面,注意evict中没丢会空指针,所以evict多加一个判断)
同一个pageId可能有多条log,最老的beforeimage才是正确的(page出去过后before就错了)
修改了还在pool中的(No steal时只有这一个),直接recoverPages(tid) 对dirty把磁盘中读出来并覆盖
TestAbort and TestAbortCommitInterleaved sub-tests of the LogTest system test.
Recovery
针对未commit的事务,回滚这些事务
针对已commit但可能还没同步写入磁盘,再次写回以确定一致性
问题:flushAllPages中flushPage时会清除Dirty标记,清除后事务commit时flushPages(tid)就不会再次移出该page,导致pool中的beforeimage并不会更新 TestCommitAbortCommitCrash测出来的(第二次看,最简单的方法就是把setbeforeimage放到flushPage的结尾)
开源代码在commit时flushPages(tid)更新所有的old,该方案应该是错的,会影响还在进行中的其他事务
pool什么时候会被移出? 页面不足时 也就是正常情况下是会在evict调用flushpage,之后一定会removepage,之后再次读入时oldpage就是最新的(对于进行中的当前事务oldpage是错的,但log中存了正确的);也就是正常逻辑下不会出错,但flushAllPages会。所以需要在flushAllPages调用flushpage后也强制removepage一次就可以了
总结 基于java语言,实现一个简易事务支持的关系型数据库
实现基本的遍历、连接、聚合和删除等基本操作算子 ,以及基于直方图的查询优化
实现BufferPool缓存Page,且实现基于LRU 的页面淘汰机制
实现页面级 的共享锁、排他锁和锁升级,实现可串行化 的并发策略
实现多种死锁检测算法:Timeout 、Wait-for Graph 、 Global Orderings (wait-die)
基于UNDO日志实现STEAL/NO FORCE 策略,提供更灵活的缓冲区管理
实现基本的WAL(Write-Ahead Logging)策略实现事务回滚与恢复
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/Cscprx/article/details/123418692
github
Code
wind/SimpleDB - 码云 - 开源中国 (gitee.com) 风在哪个人博客 (wygandwdn.cn)
SimpleDb 实验报告_simpledb实验_跳着迪斯科学Java的博客-CSDN博客
MIT6.830 SimpleDB Lab1