GPT摘要
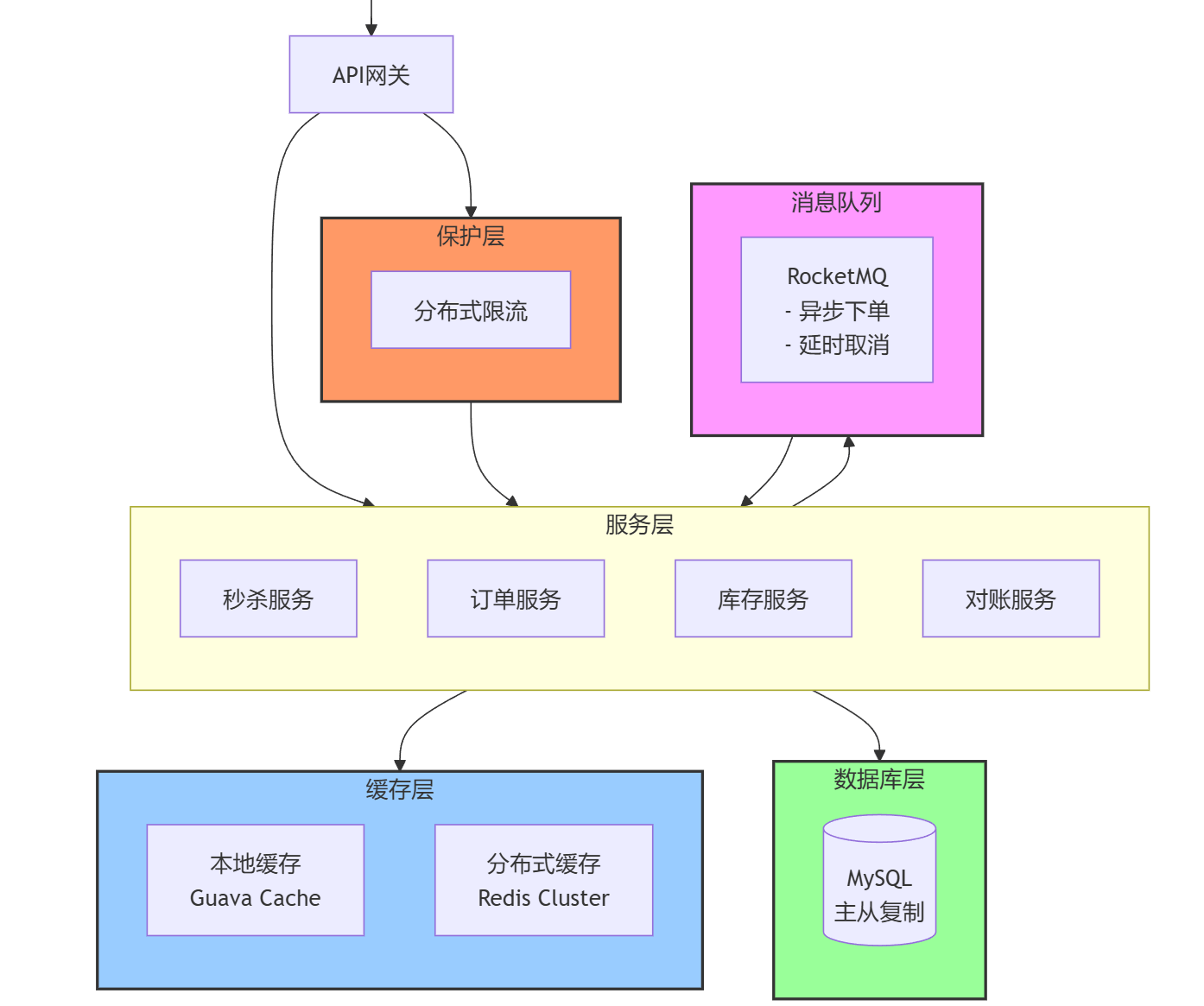
本文介绍了秒杀系统的关键优化技术,重点解决高并发下系统的稳定性、性能和数据一致性问题。主要优化措施包括: 1. 分布式限流 :基于Redis的令牌桶算法实现精准流量控制,通过注解和AOP实现接口级限流,防止瞬时流量击垮系统。 2. 订单超时处理 :利用RocketMQ延时消息实现未支付订单的自动取消和库存释放,确保库存数据准确性。 3. 多级缓存优化 :引入Guava本地缓存与Redis形成两级缓存,加速库存耗尽判断,减少Redis访问压力。 4. 库存对账机制 :通过动态水位线策略对Redis与数据库库存进行一致性校验,包括核心公式”Redis库存 + 预占库存 = 数据库库存”,并实现自动重试和告警功能,确保数据最终一致。 这些技术共同提升了系统的健壮性、可靠性和响应速度,使其能有效应对海量并发请求,同时保持高性能和数据准确性。
从零开始实现秒杀系统(四):系统优化篇 引言 在前三篇文章中,我们从基础版本开始,通过引入Redis缓存和RocketMQ消息队列,逐步构建了一个高性能的秒杀系统。然而,在面对海量用户同时抢购时,系统仍然面临着几个关键挑战:如何有效控制流量、如何保证数据一致性、如何处理超时订单,以及如何进一步提升系统性能。
本文作为系列的第四篇,将介绍几种关键的系统优化技术,使我们的秒杀系统更加健壮和高效。
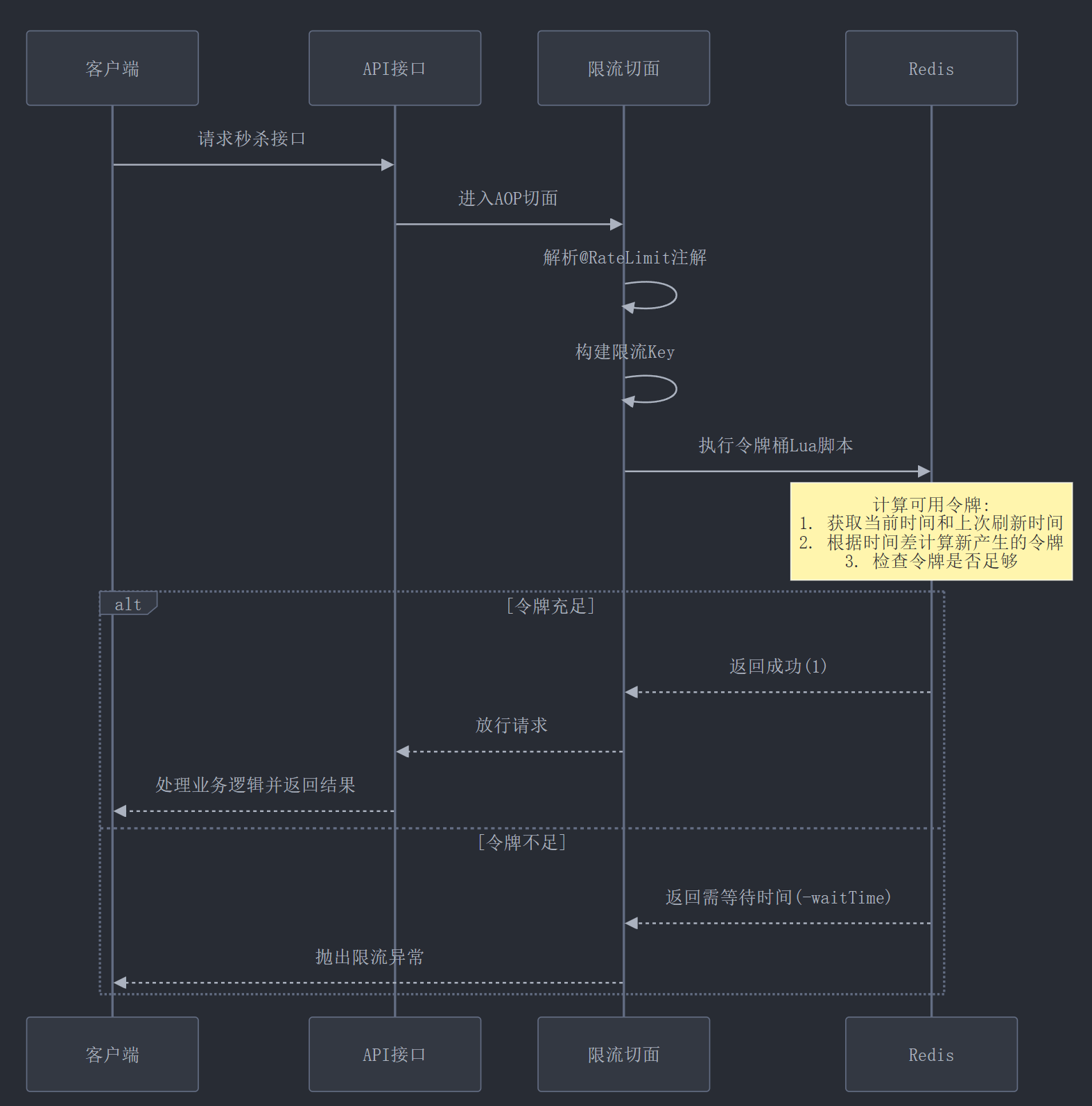
系统优化核心技术 一、基于Redis的分布式限流保护 在高并发场景下,没有限流保护的系统很容易被瞬时流量击垮。我们实现了一个基于Redis的分布式令牌桶限流机制,可以有效控制接口的访问频率。
1.1 限流注解设计 首先,我们设计了一个简单易用的注解,可以轻松地为任何接口添加限流功能:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface RateLimit {key () default "" ;type () default RateLimitType.USER;double rate () default 1.0 ;int capacity () default 5 ;int tokens () default 1 ;message () default "请求过于频繁,请稍后再试" ;enum RateLimitType {
1.2 Redis令牌桶算法实现 我们使用Lua脚本在Redis中实现了令牌桶算法,确保限流操作的原子性:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 @Component @Slf4j public class RedisRateLimiter {@Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;private DefaultRedisScript<Long> tokenBucketScript;@PostConstruct public void init () {new DefaultRedisScript <>();new ResourceScriptSource (new ClassPathResource ("scripts/token_bucket.lua" )));public long tryAcquire (String key, double rate, int capacity, int requested) {try {long now = System.currentTimeMillis();Long result = redisTemplate.execute(return result != null ? result : -1 ;catch (Exception e) {"Error executing token bucket script for key: {}" , key, e);return -1 ;
其中,token_bucket.lua脚本实现了令牌桶核心算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 local key = KEYS[1 ]local rate = tonumber (ARGV[1 ])local capacity = tonumber (ARGV[2 ])local now = tonumber (ARGV[3 ])local requested = tonumber (ARGV[4 ])local bucket = redis.call('hmget' , key, 'last_refresh' , 'tokens' )local last_refresh = tonumber (bucket[1 ]) or 0 local tokens = tonumber (bucket[2 ]) or capacitylocal elapsed = math .max (0 , now - last_refresh)local new_tokens = math .min (capacity, tokens + (elapsed / 1000.0 ) * rate)if new_tokens < requested then local wait_time = math .ceil ((requested - new_tokens) * 1000 / rate)return -wait_timeelse local remaining = new_tokens - requested'hmset' , key, 'last_refresh' , now, 'tokens' , remaining)'expire' , key, 60 ) return 1 end
1.3 限流切面的应用 使用AOP技术自动拦截带有@RateLimit注解的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 @Aspect @Component @Slf4j public class RateLimitAspect {@Autowired private RedisRateLimiter redisRateLimiter;@Before("@annotation(com.example.seckill.annotation.RateLimit)") public void rateLimit (JoinPoint point) {MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();RateLimit rateLimit = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(RateLimit.class);String key = buildRateLimitKey(rateLimit, point);long waitTime = redisRateLimiter.tryAcquireWithWaitTime(if (waitTime > 0 ) {String message = rateLimit.message();if (waitTime > 1000 ) {",需等待" + (waitTime / 1000 ) + "秒" ;throw new RateLimitException (message);private String buildRateLimitKey (RateLimit rateLimit, JoinPoint point) {StringBuilder key = new StringBuilder ("rate_limit:" );if (!rateLimit.key().isEmpty()) {":" );else {"." )":" );switch (rateLimit.type()) {case USER:"user:" ).append(point.getArgs()[0 ]);break ;case IP:HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) "ip:" ).append(getClientIp(request));break ;case GLOBAL:"global" );break ;return key.toString();
应用限流:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @PostMapping("/{userId}/{goodsId}") @RateLimit( key = "seckill", type = RateLimit.RateLimitType.IP, rate = 0.2, // 每5秒允许1个请求 capacity = 1, tokens = 1, message = "操作频率超限,请稍后再试" ) public Result<String> seckill ( @PathVariable("userId") Long userId, @PathVariable("goodsId") Long goodsId) {@GetMapping("/result/{userId}/{goodsId}") @RateLimit( key = "result", type = RateLimit.RateLimitType.USER, rate = 1.5, // 每秒1.5个请求 capacity = 3, tokens = 1, message = "查询太频繁,请稍后再试" ) public Result<Map<String, Object>> getSeckillResult ( @PathVariable("userId") Long userId, @PathVariable("goodsId") Long goodsId) {
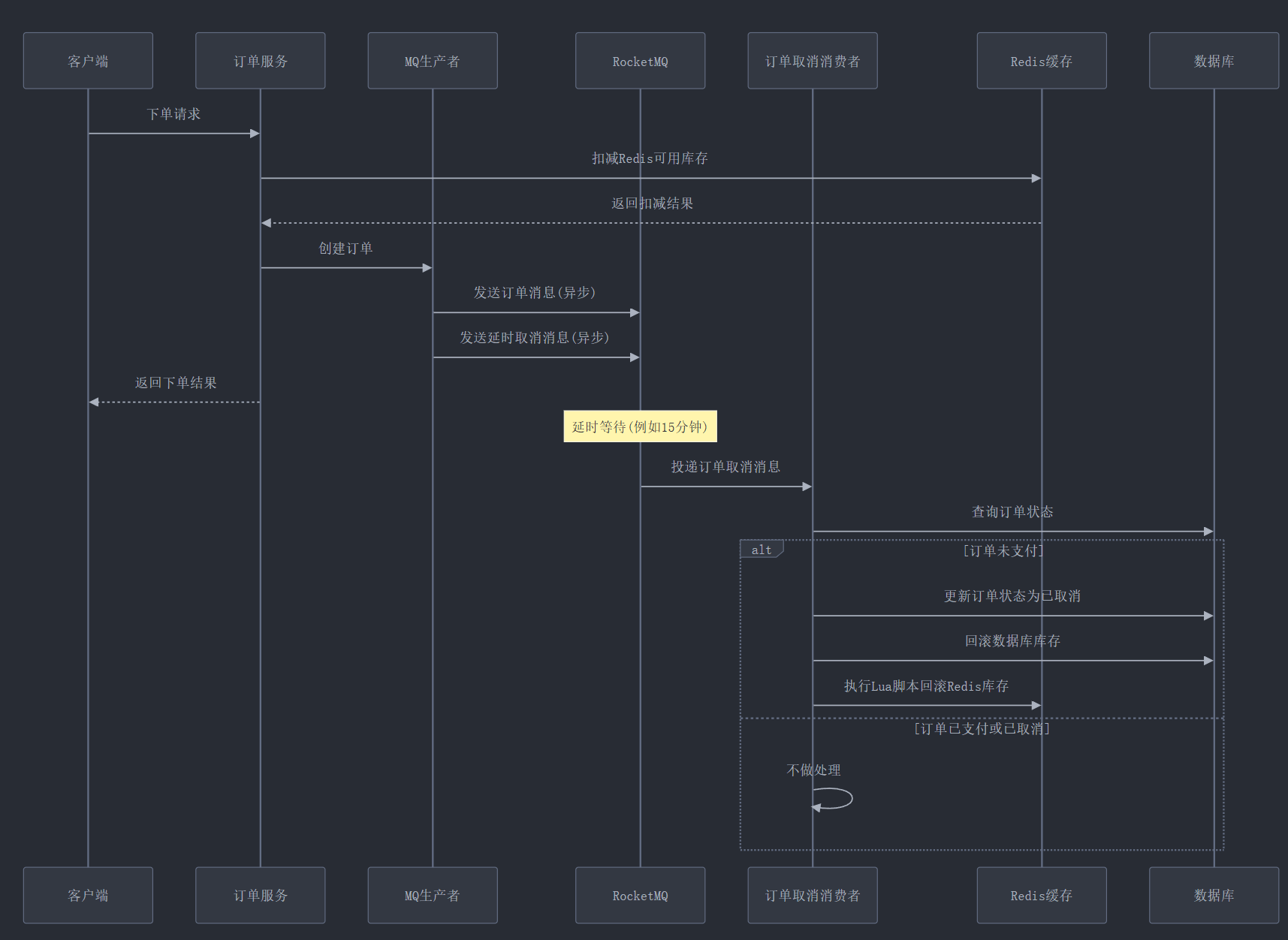
二、基于RocketMQ延时消息的订单超时处理 在秒杀系统中,未支付的订单需要在一定时间后自动取消并释放库存。我们使用RocketMQ的延时消息实现了这一功能。
2.1 订单创建时发送延时消息 在订单创建成功后,我们发送一条延时消息,用于触发订单超时取消:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public void sendOrderCancellationMessage (String transactionId, int delayLevel) {"Sending order cancellation message for transaction: {}, delayLevel: {}" , new SendCallback () {@Override public void onSuccess (SendResult sendResult) {"Order cancellation message sent successfully for txId: {}" , transactionId);@Override public void onException (Throwable throwable) {"Failed to send order cancellation message for txId: {}" ,
RocketMQ支持18个不同的延时等级,我们可以根据业务需要选择合适的延时级别。
2.2 订单取消消费者实现 消费者接收到延时消息后,处理订单取消和库存回滚:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 @Slf4j @Component @RocketMQMessageListener( topic = MQProducer.TOPIC_ORDER_CANCEL, consumerGroup = "order-cancellation-consumer-group" ) public class OrderCancellationConsumer implements RocketMQListener <String> {@Autowired private OrderService orderService;@Autowired private RedisService redisService;@Autowired private GoodsDao goodsDao;private static final DefaultRedisScript<Long> ROLLBACK_STOCK_REDIS_SCRIPT = new DefaultRedisScript <>("local stock = redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) " +"if stock then " +" redis.call('incr', KEYS[1]) " +"end " +"local reserved = redis.call('get', KEYS[2]) " +"if reserved and tonumber(reserved) > 0 then " +" redis.call('decr', KEYS[2]) " +"end " +"return 1" , Long.class);@Override public void onMessage (String transactionId) {"Received order cancellation message for transaction: {}" , transactionId);try {catch (Exception e) {"Error processing order cancellation" , e);@Transactional public void processOrderCancellation (String transactionId) {SeckillOrder order = orderService.getOrderByTransactionId(transactionId);if (order == null ) {"Order not found for cancellation, transactionId: {}" , transactionId);return ;if (order.getStatus() != 0 ) {"Order already processed (paid or cancelled), transactionId: {}" , return ;boolean success = orderService.cancelOrder(transactionId);if (success) {"Order cancelled successfully: {}" , transactionId);else {"Failed to cancel order: {}" , transactionId);private void rollbackRedisStock (Long goodsId) {"" + goodsId),"" + goodsId)
三、多级缓存优化库存查询 为了进一步提高性能,我们实现了基于Guava Cache的本地缓存,与Redis形成多级缓存架构。本地的guava可以进一步加速无库存的判断,为了简化系统库存管理,具体的库存数量信息不使用guava进行存储,guava只用于判断库存是否耗尽。
1 2 3 4 5 private final Cache<Long, Boolean> localSoldOutCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()1000 ) 5 , TimeUnit.MINUTES)
在进行库存判断是否耗尽时,先优先从本地guava中判断,减少对redis的依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 private void setGoodsOver (Long goodsId) {"" + goodsId, true );true );"Goods {} marked as sold out in both Redis and local cache" , goodsId);private boolean isGoodsOver (Long goodsId) {Boolean isOver = localSoldOutCache.getIfPresent(goodsId);if (isOver != null && isOver) {return true ;boolean isSoldOutInRedis = redisService.exists(SeckillKey.isGoodsOver, "" + goodsId);if (isSoldOutInRedis) {true );"Goods {} sold-out status loaded from Redis to local cache" , goodsId);return isSoldOutInRedis;
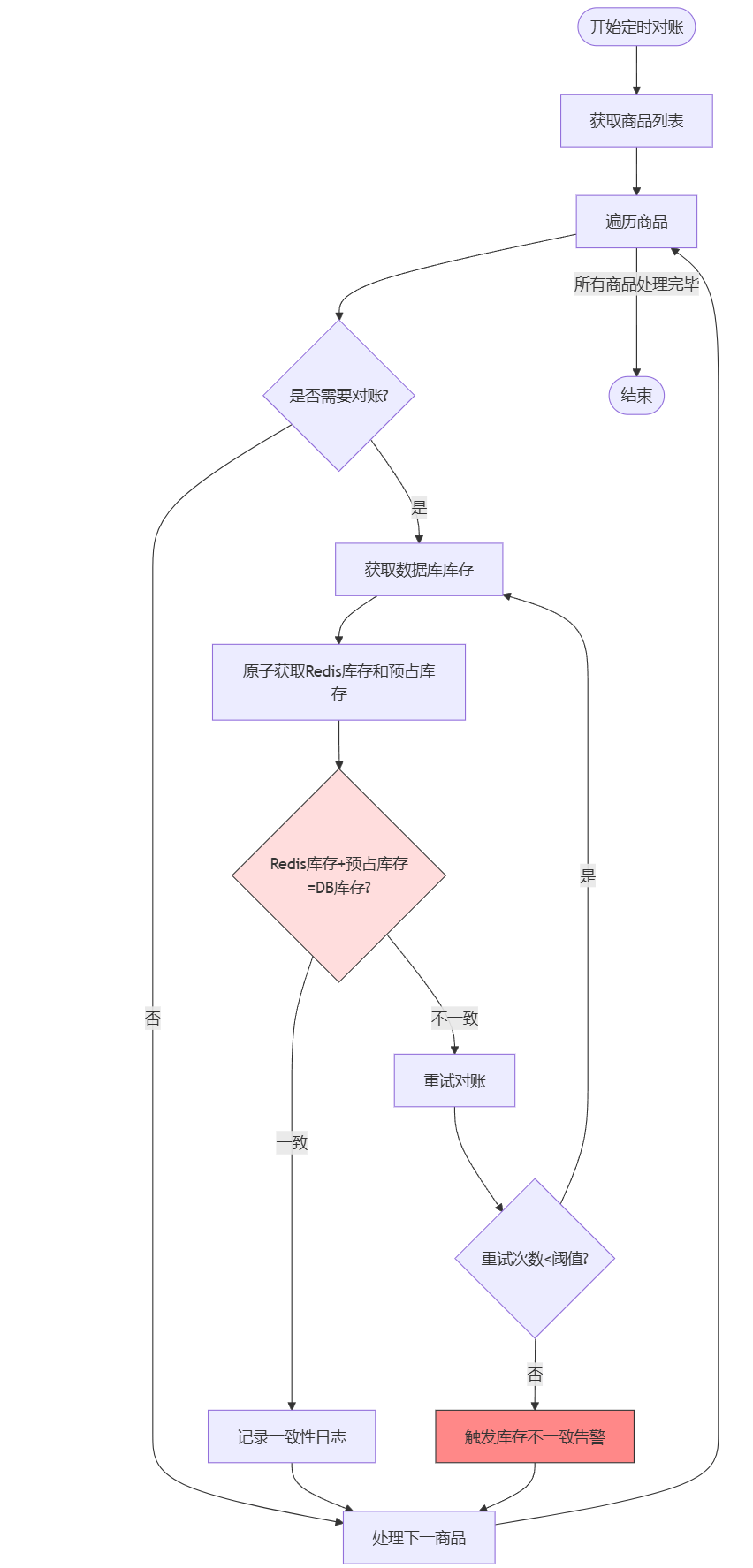
四、库存数据一致性对账机制 为了解决Redis与数据库库存可能出现的不一致问题,我们实现了一套库存对账机制。以监控系统缓存和数据库中数据一致性,并在不一致出现时及时告警。
4.1 库存模型设计 为确保数据一致性,我们设计了库存模型:
1 Redis库存 + Redis预占库存 = 数据库总库存
Redis库存 :可售卖的实时库存Redis预占库存 :已在Redis减少但尚未在数据库落库的预占量数据库总库存 :真实的最终库存数据
库存状态流转:
秒杀请求扣减Redis可用库存(goodsStock)并增加预占库存(reservedStock)
MQ消费减少数据库库存,并减少对应的Redis预占库存
这种设计确保了即使在消息处理过程中存在延迟,系统仍然能实现一致性对账。
4.2 对账机制实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Service @Slf4j public class StockReconciliationService {@Autowired private GoodsService goodsService;@Autowired private RedisService redisService;private static final int ALERT_THRESHOLD = 3 ; private static final int LOW_STOCK_THRESHOLD_PERCENTAGE = 30 ; private static final boolean RECONCILE_ALL_ITEMS = true ; private static final long RETRY_DELAY_MS = 1000 ; private static final String GET_STOCK_VALUES_SCRIPT = "local stockValue = redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) " +"local reservedValue = redis.call('get', KEYS[2]) " +"local result = {} " +"if stockValue == false then result[1] = '' else result[1] = stockValue end " +"if reservedValue == false then result[2] = '' else result[2] = reservedValue end " +"return result" ;@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1 * 60 * 1000) public void scheduledReconciliation () {"Starting scheduled stock reconciliation" );if (goodsList == null || goodsList.isEmpty()) {"No goods found for reconciliation" );return ;for (GoodsVo goods : goodsList) {if (shouldReconcile(goods)) {
4.2.1 水位线对账策略 为了减少系统负担,我们基于水位线策略选择性地对商品进行对账:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 private boolean shouldReconcile (GoodsVo goods) {if (RECONCILE_ALL_ITEMS) {return true ;Integer redisStock = redisService.get(SeckillKey.goodsStock, "" + goods.getId());if (redisStock == null ) {return false ;int initialStock = goods.getTotalStock();if (initialStock <= 0 ) {return true ; int stockPercentage = (redisStock * 100 ) / initialStock;return stockPercentage <= LOW_STOCK_THRESHOLD_PERCENTAGE;
4.2.2 对账流程与重试机制 对账核心逻辑包含了原子性数据采集、一致性校验和自动重试机制:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public void reconcileStock (Long goodsId) {"Reconciling stock for goods ID: {}" , goodsId);int retryCount = 0 ;boolean isConsistent = false ;while (!isConsistent && retryCount < ALERT_THRESHOLD) {try {GoodsVo goods = goodsService.getGoodsVoByGoodsId(goodsId);if (goods == null ) {"Failed to get goods info for ID: {} during reconciliation" , goodsId);return ;Integer dbStock = goods.getStockCount();String stockKey = redisService.getRealKey(SeckillKey.goodsStock, "" + goodsId);String reservedKey = redisService.getRealKey(SeckillKey.reservedStock, "" + goodsId);Integer redisStock = values.get(0 ) != null && !values.get(0 ).toString().isEmpty() ? 0 ).toString()) : null ;Integer reservedStock = values.get(1 ) != null && !values.get(1 ).toString().isEmpty() ? 1 ).toString()) : 0 ;if (redisStock == null ) {"Redis stock not found for goods: {}" , goodsId);return ;if (!isConsistent) {"Stock inconsistency detected for goods {}: Redis({}) + Reserved({}) = All({}) != DB({}), retry: {}/{}" , if (retryCount >= ALERT_THRESHOLD) {else {else {"Stock reconciliation successful for goods {}: Redis({}) + Reserved({}) = DB({})" , catch (Exception e) {"Error during stock reconciliation for goods: {}, retry: {}/{}" ,
4.2.3 告警机制 当多次对账依然不一致时,系统会触发告警机制:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private void sendAlert (Long goodsId, Integer redisStock, Integer reservedStock, Integer dbStock) {"ALERT: Persistent stock inconsistency for goods {}: Redis({}) + Reserved({}) != DB({})" ,
总结 本文介绍了秒杀系统的几个关键优化技术:
基于Redis的分布式限流 :使用令牌桶算法实现精确的流量控制,保护系统免受流量峰值冲击基于RocketMQ的延时消息 :实现可靠的订单超时自动取消,确保库存正确释放多级缓存架构 :结合Guava本地缓存和Redis分布式缓存,进一步提升系统性能库存对账机制 :确保Redis与数据库之间的库存数据一致性
通过这些优化,我们的秒杀系统不仅能够应对高并发场景,还能在保证性能的同时确保数据一致性和系统可靠性。
本文源码已开源在GitHub:Goinggoinggoing/seckill
如有疑问或建议,欢迎在评论区讨论!